Breast Diseases
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer refers to the presence of tumor masses composed of cancerous cells in the breast, forming palpable lumps. The exact cause of breast cancer is not yet fully understood. However, through various studies comparing breast cancer patients with non-patients, differences have been observed, leading to the identification of risk factors.
Risk factors for breast cancer include female hormones (estrogen), age and childbirth experience, breastfeeding, alcohol consumption, radiation exposure, and family history of breast cancer.
Treatment Methods
The primary treatment for breast cancer involves surgical removal of the cancerous tissue to prevent its spread to other organs. This is done to prevent cancer cells from metastasizing to other parts of the body.
There are two main surgical approaches for breast cancer: "breast-conserving surgery," which removes the cancer while preserving some healthy breast tissue, and "mastectomy," which involves removing the entire breast when extensive disease makes breast conservation difficult. In recent times, breast-conserving surgery has become more common due to increased early detection of breast cancer cases.
Following surgery, additional treatments such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy may be administered as adjuvant therapy. The choice of adjuvant therapy is determined based on the biological characteristics of the tumor cells, disease progression, prognosis, patient's age or menopausal status, and overall health.
Breast Cancer Benign Tumors
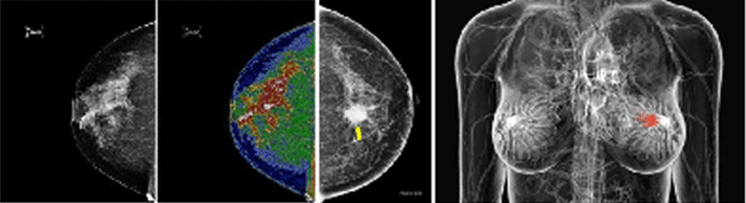
Diagnosis is conducted through breast examination, mammography, and breast ultrasound. If a lump is felt during the examination or if there are suspicious findings such as abnormal shadows, asymmetry, microcalcifications, or dense breast tissue on mammography, a breast ultrasound is also performed.
Depending on the appearance and characteristics observed during the breast ultrasound, a tissue biopsy may be necessary.
Treatment Methods
A minimally invasive procedure called "mammatome" is used to remove the tumor from the breast with only local anesthesia, resulting in minimal scarring. Mammatome is a surgical technique that alleviates concerns about surgery for women.
The procedure involves making a small incision of 5-7 mm, inserting a mamma-tome device, and removing the tumor, leaving almost no scar. The procedure typically takes 30 minutes to 1 hour, and since it is performed under local anesthesia, the risk of side effects or complications is low, allowing for a quick return to daily activities.
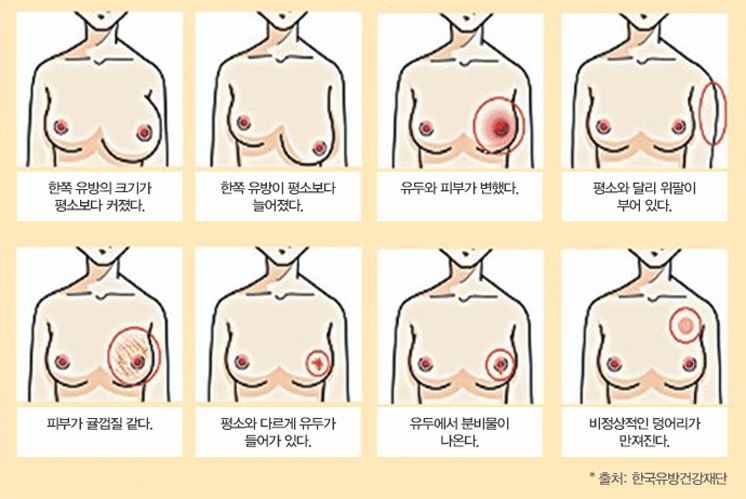
Breast Cancer Self-Diagnosis
Thyroid Diseases
Thyroid Cancer
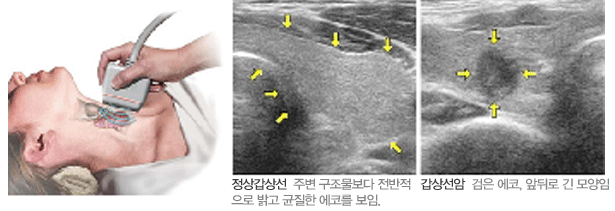
The thyroid is an endocrine gland located in the front of the neck, producing, storing, and secreting thyroid hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. Thyroid nodules are relatively common and can be classified into benign, malignant (cancerous), and cystic nodules. Among these, malignant nodules account for about 5% of thyroid nodules.
Most cases of thyroid cancer are classified as papillary carcinoma (80%), followed by follicular carcinoma (15%), and other types of cancer are also observed. Common symptoms include voice changes, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and breathing difficulties.
Treatment Methods
The primary treatment for thyroid cancer is surgery. The extent of the surgery is determined based on the patient's age, tumor size, invasion into surrounding tissues, extent of lymph node metastasis, and presence of distant metastasis.
After surgery, hormone replacement therapy is given to address hormone deficiency and suppress recurrence of thyroid cancer.
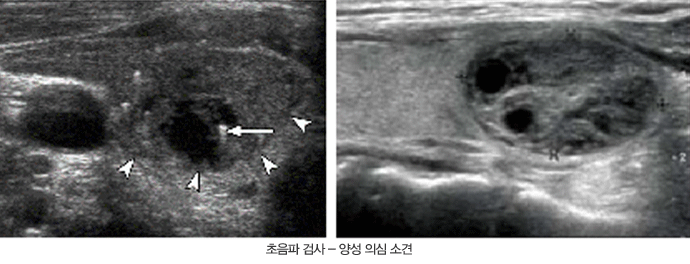
Benign Thyroid Nodules
Benign nodules usually do not cause any symptoms until they are incidentally discovered. In most cases, benign nodules do not cause harm to the body and are considered as cosmetic concerns.
Occasionally, pain may occur if bleeding within the nodule or cystic degeneration (liquefaction) of a part of the nodule happens.
Treatment Methods
Diagnosis is made through ultrasound examination, cytology, tissue biopsy, thyroid hormone measurement, and thyroid scan.
Since benign nodules do not pose any harm to the body, they do not require specific treatment.
However, if the size of the nodule causes compression symptoms on surrounding tissues, surgical removal is recommended.